Breast Augmentation
Breast augmentation continues to be one of the most popular procedures for women with almost 300,000 performed in the United States. According to the American Society of Plastic Surgery, 72% of breast augmentations were performed with silicone gel implants versus 28% with saline implants.
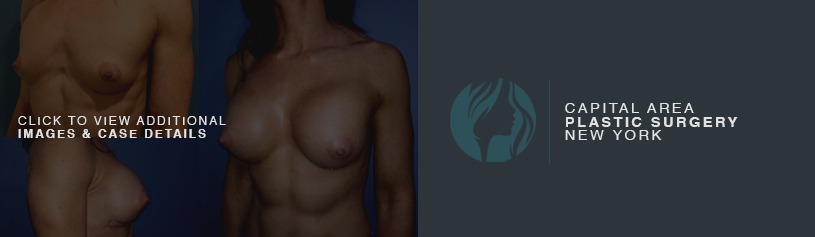
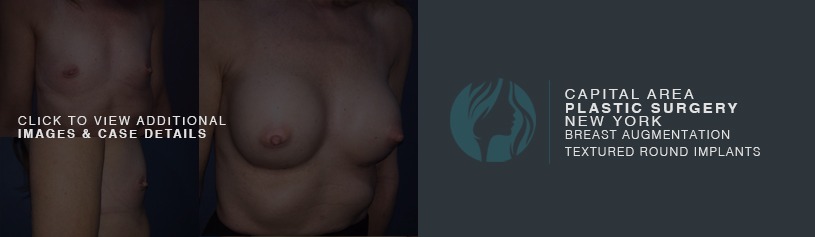
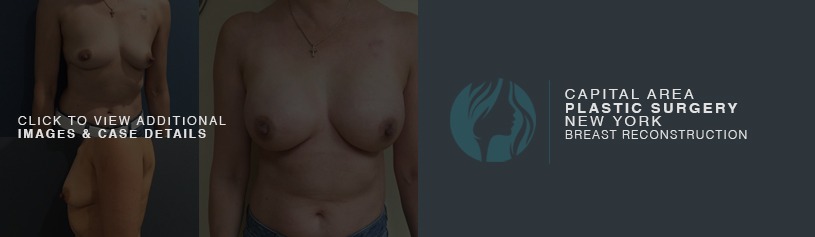
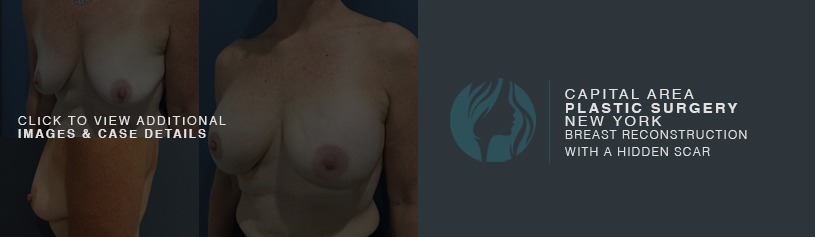
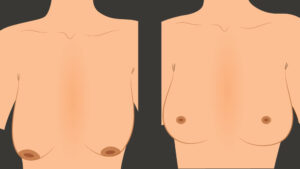
Breast augmentation is a cosmetic procedure with the aim of increasing the size, changing the shape or fullness of a woman’s breasts. Breast implants are placed in the breast pocket under the breast tissue or under the muscle during the surgery.
Who is a candidate?
Any healthy woman who is able to undergo breast augmentation. Breast augmentation is available to any female over the age of 18 years old without the consent of an adult. A female’s growth should be complete and stable. If choosing silicone gel implants and you are less than 22 years of age it would be considered an off label use.
That being said, we recommend a thorough understanding of the risks, alternatives and benefits of undergoing a breast implant augmentation and possess the maturity to make the right decision.
How is it performed?
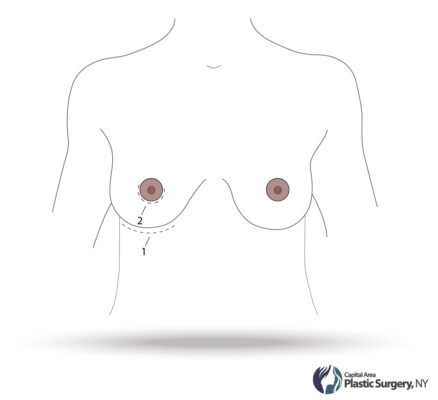
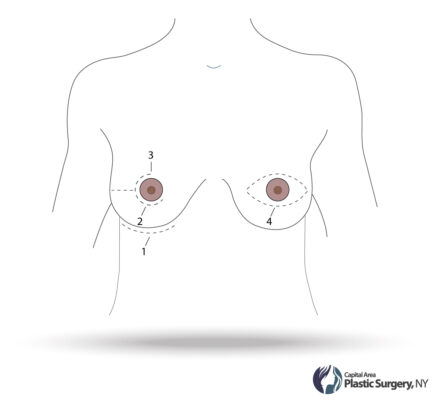
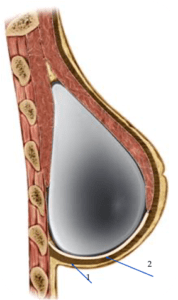
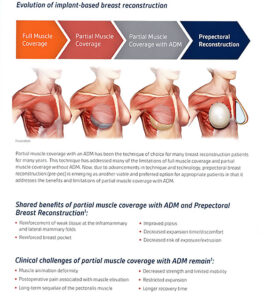
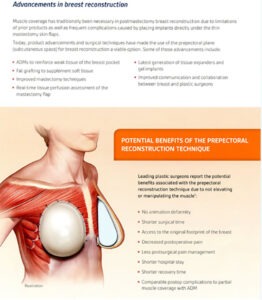
An incision is made in the fold of the (inframammary) or along the areola of the nipple (peri-areolar) most frequently. Some surgeons will also make an incision in the axilla (trans-axillary). The implant is then placed in a pocket that is dissected underneath the breast tissue (subglandular) or the pectoralis major muscle (submuscular).
Dr. Koumanis will discuss incision options with you and the advantages and disadvantages associated with the different methods. The biggest advantage of putting them under the muscle is that there is less chance of a capsular contracture (hardening of the breast capsule around the implant).
The surgery usually takes 1.5 to 2 hours and is performed most frequently under general anesthesia but sometimes under intravenous conscious sedation where the patient does not require a breathing tube and is given medication to make them very drowsy.
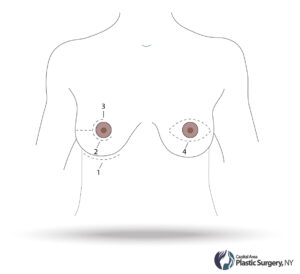
Where is the incision made?
The most common place for the incision is hidden just under the breast fold. The incision is usually under 2 inches. Another common place is a small incision around the areola if the patient is a candidate. The implants are then introduced through this small space in a safe and sterile manner.